20 May 2024
Herbicide resistance update for grass weeds

Vijaya Bhaskar, Teagasc Oak Park, tells us how difficult-to-control grass weeds such as Italian ryegrass, blackgrass, wild oats and bromes pose herbicide resistance problems on our tillage farms.
The 2023 testing of resistance-suspect populations of these weeds revealed a worrying situation, as 60% (34 out of 57 samples) were found to be resistant to a wide range of herbicides.
Italian ryegrass
17 different Italian ryegrass populations grown alongside a sensitive population were sprayed at the two to three-leaf stage with label rates of ACCase (Axial, Falcon, Stratos Ultra, Centurion Max) and ALS (Pacifica Plus or Monolith, Broadway Star) herbicides (Figure 1).
- 15 out of 17 populations tested were resistant.
- All 15 populations were ALS-resistant and 12 of those were also ACCase-resistant.
- Populations that developed resistance to Stratos Ultra also had an impact on the efficacy of Centurion Max, resulting in no chemical options within crops for four populations.
- Target-site resistance was the main mechanism for populations resistant to ALS herbicides. However for ACCase, target-site (for populations cross-resistant to all ACCase herbicides) and metabolic resistance (for populations resistant to Axial and/or Falcon) were both involved.


Figure 1: Overhead view of test trays showing the symptoms of sensitive and resistant populations of Italian ryegrass 28 days post-treatment with ACCase Axial, Falcon, Stratos Ultra and Centurion Max and ALS Pacifica Plus or Monolith and Broadway Star all applied at the recommended rate. Where treated-plants are absent from a square full control was achieved.
Blackgrass
12 different blackgrass populations grown alongside a sensitive population were sprayed at the two to three-leaf stage with label rates of ACCase (Falcon, Stratos Ultra, Centurion Max) and ALS (Pacifica Plus) herbicides (Figure 2).
- 9 out of 12 populations tested were resistant.
- 5 populations were ACCase/ALS-resistant, 3 populations were ACCase-resistant and 1 population was ALS-resistant
- Centurion Max in this case remained effective on all populations, including populations that developed full resistance to Stratos Ultra (eg. Meath-1, Cork-1).
- Target-site resistance was the main resistance mechanism for populations resistant to ACCase and/or ALS herbicides.
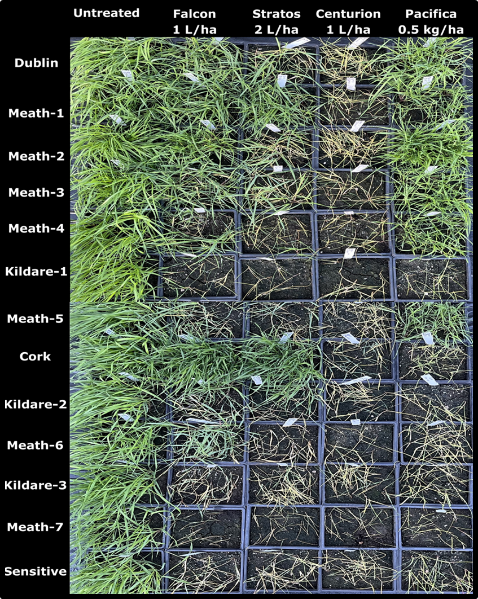

Figure 2: Overhead view of test trays showing the symptoms of sensitive and resistant populations of blackgrass 28 days post-treatment with ACCase Falcon, Stratos Ultra and Centurion Max and ALS Pacifica Plus all applied at the recommended rate. Where treated-plants are absent from a square full control was achieved.
Spring wild oats
14 different wild oat populations were sprayed at the three to four-leaf stage with label rates of ACCase (Axial, Falcon, Stratos Ultra) and ALS (Pacifica Plus) herbicides (Figure 3).
- 10 out of 14 populations tested were ACCase-resistant, with none ALS resistant at this point.
- Different ACCase cross-resistance patterns were found, with some populations resistant to Axial, Falcon and Stratos (eg. Carlow), some resistant to Axial and Falcon (eg. Wexford-1, Wexford-2), some resistant to Falcon (eg. Dublin-2) and some resistant to Falcon and Stratos (eg. Kilkenny-2).
- Target-site resistance was the main resistance mechanisms, with specific mutations responsible for cross-resistance patterns.


Figure 3: Overhead view of test trays showing the symptoms of suspected resistant populations of wild oats 28 days post-treatment with ACCase Axial, Falcon, Stratos Ultra and ALS Pacifica Plus all applied at the recommended rate. Where treated-plants showed severe stunting, discoloration or yellowing and browning (death) of foliage full control was achieved.
Bromes
14 different bromes (including sterile, great and soft) were sprayed at the two to three-leaf stage with label rates of ACCase (Falcon, Stratos Ultra, Centurion Max) and ALS (Pacifica Plus, Broadway) herbicides (Figure 4).
- Both ACCase and ALS herbicides were very effective on all populations.
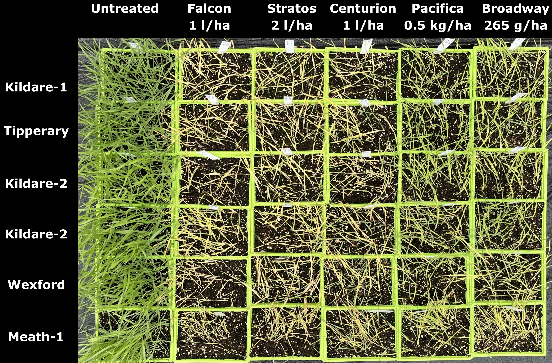
Figure 4: Overhead view of test trays showing the symptoms of suspected resistant populations of bromes 28 days post-treatment with ACCase Falcon, Stratos Ultra and Centurion Max and ALS Pacifica Plus and Broadway Star all applied at the recommended field rate. Where treated-plants showed severe stunting, discoloration or yellowing and browning (death) of foliage full control was achieved.
In brief
Farms where Italian ryegrass and blackgrass are present, should be treated as resistance-suspect, and samples sent for analysis prior to harvest. A zero tolerance approach should be taken to avoid weed seed being returned.
Farms where ACCase-resistant spring wild oats is present have only one option available: ALS (Pacifica or Broadway) herbicides. This is a crisis situation. These should be carefully used in conjunction with hand rogueing to reduce the seedbank number. Continued use of the one product will lead to resistance.
No full herbicide-resistant brome was detected. Both ALS (Pacifica, Broadway) and ACCase (Falcon, Stratos) have been found to be effective when applied at full label rates on small and actively growing plants, but the loss of sensitivity with lower rates (previous work) is worrying. Cultural control methods (stale seedbeds, rotation, later sowing etc.) should be practiced where brome is present.
The limited opportunities for autumn pre-emergence use, and the on-going wet weather challenges will affect the timely spring weed control programme this season. Products used now should be reviewed based on weed spectrum, crop type and growth stages.
Increased vigilance, resistance testing and integrated approaches (cultural control and judicious use of herbicides) are essential to combat increasing resistance threat.
